Excess hair loss that causes your hairline to recede can significantly impact your confidence, but remember you are not alone. Both men and women typically experience a receding hairline by the time they reach 50. Many people are dealing with thinning hair due to poor diet patterns, stress, aging, genetics, and hormone issues. You might also notice that your hairline has moved upwards from the forehead, forming a clear pattern or an uneven shape. You need not be worried that such hairline receding would lead to male pattern baldness, as there are safe and effective treatments available to restore a fuller hairline. Continue reading this write-up to learn more about a receding hairline, its signs, stages, treatment options, and prevention tips.
What Is a Receding Hairline?
A receding hairline occurs when your scalp’s front part begins to thin gradually and moves upwards. It is referred to as androgenetic alopecia, one of the visible signs that indicate the development of pattern baldness [1]. Even though people tend to lose hair as they get older, it might sometimes be an indicator of a lifestyle disease or an underlying health issue. For males, the hair loss might begin near the temples and would gradually form a V or M shape. Females would experience general hair thinning in their crown region instead of a dramatic hairline recession near the forehead and temples. Despite such significant differences, both types of receding hairlines can drastically alter the way one feels about their overall appearance and cause emotional turmoil [2].
Early Signs of a Receding Hairline
- If you have one or more of the signs listed below, it is an indicator of the onset of a receding hairline that needs immediate medical attention.
- Appearance of a thin band on the skin in a lighter tone running between the temples along the forehead.
- Small rashes on the skin, yellow or red color on the hairline area affected by hair loss.
- Full balding effect on the front that runs backwards on the scalp.
- Visible hair thinning and hair loss along the temples, developing in a clear-cut V or M shape.
- Your temples might have visible hair thinning.
- Occurrence of bad patches and hair loss in a zigzag pattern near the hairline.
- You might have a subtle receding hairline or a well-pronounced receding hairline with no strands of hair on the crown part of your head.
Receding Hairline Stages (Norwood Scale) – 7 stages
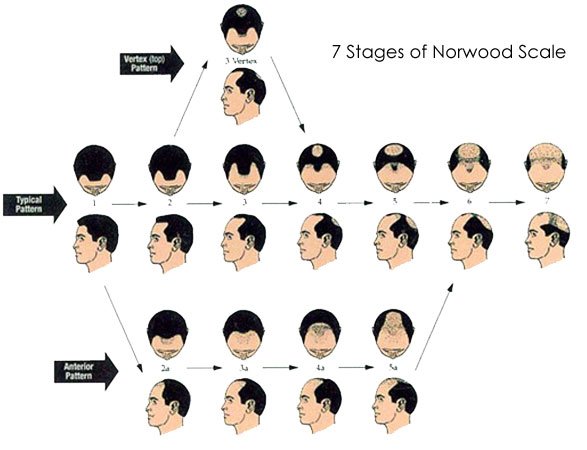
Your doctor would identify the progression of your receding hairline based on the stages specified by a standard system referred to as the Hamilton-Norwood Scale [3]. This scale classifies the receding of the hairline through stages varying from the 1st Stage to the 7th Stage based on the severity of hair fall. Here are the 7 stages of a receding hairline.
- 1st Stage: You will have a normal-looking hairline with no obvious signs of recession or thinning.
- 2nd Stage: There might be a subtle hint of hairline receding near the forehead. However, it will not be noticeable and will not affect your overall appearance.
- 3rd Stage: During this Norwood scale stage, you will find that hair loss is much visible on the scalp’s crown area, called the vertex. Plus, the hairline will begin to recede in a subtle M pattern.
- 4th Stage: Your hairline will flaunt a more pronounced and defined M shape. And the vertex area will be visible with very minimal hair strands.
- 5th Stage: During this stage, the hairline receding in the M pattern will continue to shift upwards. It will also begin to connect with the balding regions on the scalp’s crown and front.
- 6th Stage: Both the crown and front side of the scalp would have fully merged during this stage. Your head will have visible hair only on the backside and sides of the scalp.
- 7th Stage: This stage of the Norwood scale indicates severe hairline receding at a quick pace. There would be a tiny band with hair strands located at the back and sides.
Common Causes of a Receding Hairline
There are various reasons that double up as contributing factors to a receding hairline [4]. Knowing the factors that lead to this hair loss condition would help you take well-informed steps to manage it at an early stage.
1. Aging Factor
As you get older, the hair follicles will begin to get smaller and grow shorter and finer hair. So the hair strands become naturally thin, and the density declines with time. Several studies have revealed that most men aged above 50 tend to face hair loss, and these numbers tend to increase once they reach 70. Women also face hair thinning issues soon after menopause when their hormone levels become erratic.
2. Hormonal Impact
Your hormones have a key role in influencing hair health and help in regrowth. Generally, DHT or dihydrotestosterone hormone can change the natural cycle of hair growth in males. This hormone can decrease the period of your hair growth phase and cause the production of thinner hair or combat growth altogether. Women also face extreme hair loss and visible hair thinning when hormone levels fluctuate during pregnancy, puberty, and menopause. Such hormonal changes can directly contribute to a receding hairline.
3. Genes and Family History
Both family history and genetics have a pivotal role in causing a receding hairline. If one or more of your family members has a receding hairline or pattern baldness, you are more likely to develop the same in the future. Men or women with a family history of baldness will also have a similar type of patterned hair loss.
4. Treatments and Medications
Specific medications will lead to extreme hair loss as a side effect, causing your hairline to recede. Medications used as a part of hormone therapy and other health conditions will also shrink hair follicles, causing the hairline to recede. Advanced treatments like chemotherapy will also cause heavy hair loss and shedding.
5. Lifestyle Habits
Your everyday habits can also be a culprit behind hair loss. Smoking habits will cause hair loss because the toxins present in it will decrease blood circulation to hair follicles and lead to oxidative stress [5]. Consuming a diet that doesn’t contain nutritious ingredients and has high fat content will also weaken hair follicles, causing them to shed [6].
Who Is Most at Risk of Developing a Receding Hairline?
- If you have blood relatives facing pattern baldness, causing a receding hairline, you are at a higher risk of developing it.
- The risk of experiencing a receding hairline is higher as you age. About 85% of men above 50 are prone to thinner hair.
- Men with high DHT levels are prone to develop male pattern baldness, and women in menopause face excess hair shedding.
- When compared to females, males are at a higher risk of developing a thinning hair line or patterned hair loss in a V or M shape.
Effective Prevention Tips
- Do not wear tight hairstyles like ponytails and braids that pull the follicles and cause hair loss.
- Choose supplements that contain essential vitamins and minerals that support hair growth. But, they might not be effective for genetic hair loss.
- Do not go for harsh styles that involve the use of relaxants, perming tools, hair colors, and bleach.
- Try hair massage with serums or essential oils like saw palmetto or rosemary oil to nurture the health of follicles [7].
When to Consider Hair Transplant
- People facing patterned hair loss, like androgenetic alopecia with thinning, can consider a hair transplant to restore it.
- People aged above 25 and dealing with a receding hairline can opt for a minimally invasive or invasive hair transplant.
- Men or women with good overall health and extreme hair loss in a pattern can choose a transplant.
- People with good hair texture, density, and thickness at the back or sides can get better results with transplants.
Treatment Options for Different Stages
Initial Hair Loss Stage – (1st and 2nd Stages)
- Your doctor might prescribe topical medications like Finasteride / Minoxidil for curbing hair loss and strengthening hair follicles.
- For hair issues like early thinning, LLT or Low-level laser therapy can help kindle growth at the follicular level [8].
Mid-level Hair Loss Stage – (3rd & 4th Stage)
- If facing the 3rd and 4th stages of receding hairline, your doctor would suggest hair transplants combined with other treatments for better hair density.
- PRP Treatment will be useful for encouraging hair follicles with concentrated blood plasma to promote hair regrowth [9].
Advanced Hair Loss Stage – (5th to 7th Stage)
- During these advanced stages, hair transplant procedures are a suitable solution for rectifying baldness, receding hairline, and regrowing hair [10].
- Your surgeon might suggest Direct Hair Implantation, Follicular Unit Extraction [11], and Follicular Unit Transplantation techniques involving follicular extraction and implantation for natural hair growth.
- Transplants can work well with other procedures to enhance hair density.
Wrapping Up
It doesn’t matter which stage of receding hairline you are facing, consult a hair specialist at Akruti today to bid goodbye to low confidence levels and hair loss issues.
Reference Links
- Ho CH, Sood T, Zito PM. Androgenetic Alopecia. [Updated 2024 Jan 7]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430924/ – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430924/
- American Academy of Dermatology Association – https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/hair-loss/types/frontal-fibrosing-alopecia
- Mrinal Gupta Sudhaa Skin Centre, Treatwell Clinic, Canal Road, Sidhra, Jammu, India – https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-2077.178536
- American Academy of Dermatology Association – https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/hair-loss/causes/18-causes
- Arash Babad, Delila Pouldar Foulad; Bobak Hedayati; Evyatar Evron; Natasha Mesinkovska – https://karger.com/sad/article-abstract/7/4/251/291628/The-Effects-of-Smoking-on-Hair-Health-A-Systematic
- Hironobu Morinaga, Yasuaki Mohri, Marina Grachtchouk, Kyosuke Asakawa, Hiroyuki Matsumura – https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-021-03624-x
- Panahi Y, Taghizadeh M, Marzony ET, Sahebkar A. Rosemary oil vs minoxidil 2% for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia: a randomized comparative trial. Skinmed. 2015 Jan-Feb;13(1):15-21. PMID: 25842469. – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25842469/
- Jisha K Pillai Department of Dermocosmetology, Lilavati Hospital and Research Centre, Bandra, Mumbai, India – https://jcasonline.com/role-of-low-level-light-therapy-lllt-in-androgenetic-alopecia/
- Elena E. Pakhomova, Irina O. Smirnova1: Department of Infectious Diseases, Epidemiology and Dermatovenereology, St. Petersburg State University, 199034 St. Petersburg, Russia – https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/18/6516
- Francisco Jimenez, fjimenez@mediteknia.com ∙ Majid Alam, PhDb, ∙ James E. Vogel, MD ∙ Marc Avram, MD – https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0190962221009014
- Ravi Sharma & Anushri Ranjan – https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12663-019-01245-6

